Mass
Mass of a body is the amount of matter it contains.
The SI unit of mass is kilogram(kg). Other commonly used units are gram(g) and tones(t).
1kg = 1000g
1t = 1000kg
The mass of a body doesn't change from place to place. The instrument used to measure mass is called a beam balance.
1kg = 1000g
1t = 1000kg
The mass of a body doesn't change from place to place. The instrument used to measure mass is called a beam balance.
Beam Balance:
Time
Is the gap between two occasions or events.The SI unit of time second(s). Other units used are minutes (min), hour(h),day etc.1 min = 60s
1h = 3600s
1 day = 86400s
The instruments for measuring time are clocks and watches.
Examples are volume, density, power, work, energy, weight, frequency etc.
The S.I Units of Derived Quantities
Volume
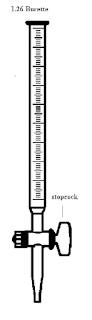
Volume is the amount of space occupied by a substance. The SI unit is cubic meter (mˆ3).Other units used are cubic centimeter (cmˆ3) and litre(l).Instruments used to measure the volume of liquids:
Measuring cylinder-used for measuring or pouring out various liquids.
How to read volume measuring instruments (precautions).
Readings are always taken at the level of the bottom of the meniscus or curved surface of the liquid. Mercury is an exception as its meniscus curves downwards.
Care should be taken to place the eye correctly to avoid parallax errors. When taking readings, the pipette and burette must be upright and the cylinder and flask must stand on a horizontal bench otherwise errors may arise from tilting.
Measuring volume of irregular objects.
The volume of an irregular solid can be determined by measuring the volume of water displaced in a measuring cylinder directly or with the aid of an overflow eureka can.
Experiment
Aim: To measure the volume of an irregular object.
Methods
By using a measuring cylinder directly
Materials and apparatus: Irregular object eg; stone, thread, measuring cylinder, eureka can and water.
Procedures
Poor a known volume of water in a burette(V1)
Tie a stone with a thread.
Immerse the tied stone in water holding the thread and record the volume (V2)
Make sure the stone is totally immersed in water. Results
Volume before introducing solid = V1
Volume after introducing solid = V2
Volume of irregular solid(V3) = V2 – V1 By using the eureka can
Procedure to follow:
Poor water into eureka can up to its spout Immerse a well tied stone in water completely
Collect the overflowed water in the water.
Use a measuring cylinder to determine the volume of water collected Observation
When a stone was introduced in an overflow can, water overflowed to the measuring cylinder.
The volume of water collected is equal to the volume of irregular object(stone)
The volume of an irregular solid can be determined by measuring the volume of water displaced in a measuring cylinder directly or with the aid of an overflow eureka can.
Experiment
Aim: To measure the volume of an irregular object.
Methods
By using a measuring cylinder directly
Materials and apparatus: Irregular object eg; stone, thread, measuring cylinder, eureka can and water.
Procedures
Poor a known volume of water in a burette(V1)
Tie a stone with a thread.
Immerse the tied stone in water holding the thread and record the volume (V2)
Make sure the stone is totally immersed in water. Results
Volume before introducing solid = V1
Volume after introducing solid = V2
Volume of irregular solid(V3) = V2 – V1 By using the eureka can
Procedure to follow:
Poor water into eureka can up to its spout Immerse a well tied stone in water completely
Collect the overflowed water in the water.
Use a measuring cylinder to determine the volume of water collected Observation
When a stone was introduced in an overflow can, water overflowed to the measuring cylinder.
The volume of water collected is equal to the volume of irregular object(stone)











0 Comments