Example 1
A sack of maize, which weighs 800N, is lifted to a height of 2m. What is work done against gravity?Data given:
Force (f) = 800N Height distance = 2m Work done = ?
Solution:
Work done (w.d) = force (f) x distance (d)
w.d = 800N x 2m
= 1600 Joules
Work done (w.d) = 1600 Joules
Example 2
A ball of mass 0.5 kg is kicked vertically upwards and rises to a height of 5m. Find the potential energy by the ball.
Data given:
Mass of the ball (Mb) = 0.5 kg Height (h) = 5m
Gravitation force (g) 10N/kg Potential energy (P.E) = ?
Solution:
Potential energy (P.E)= mgh
= 0.5kg x 10N/kg x 5m
= 25 NM
1NM= 1 Joules
Potential energy (P.E) = 25 Joules.
Data given:
Mass of the ball (Mb) = 0.5 kg Height (h) = 5m
Gravitation force (g) 10N/kg Potential energy (P.E) = ?
Solution:
Potential energy (P.E)= mgh
= 0.5kg x 10N/kg x 5m
= 25 NM
1NM= 1 Joules
Potential energy (P.E) = 25 Joules.
Example 3
A stone of mass 2kg is released from a height of 2m above the ground. Find the potential energy of the stone when it is at the height of 0.5m above the ground.Data given;
Mass of the stone (Ms) = 2kg Height released (h) = 2m Gravity (g) = 10N/kg Potential energy = (P.E) ?
Solution:
P.E at height g 2m
P.E = Mgh
= 21g x 10N/kg x 2m
P.E = 40 Joules
P.E at 2m = 40 Joules
Then P.E at height of 0.5m = 21g x 10N/kg x 0.5m
P.E at 0.5m = 10 Joules
100s of P.E = 40 Joules - 10 Joules
= 30 Joules
According to conservation of energy the loss of P.E should be equal to the gain in K.E, when the air resistance is neglected.
K.E of the stone at 0.5 above the ground = 30 Joules
Example 4
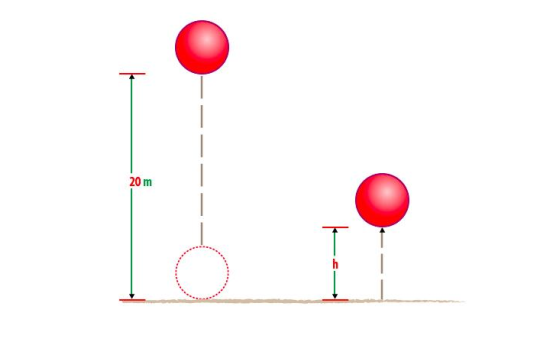
A ball of mass 0.21kg is dropped from a height of 20m. on impact with the ground it loses 30J of energy. Calculate the height which it reaches on the rebound.Data given;
Mass of ball (Mb) = 0.2kg Height dropped (h) = 20m Loose in energy (E) 30J Height which reaches=?
Solution;
Consider the figure below;
= 0.2kg x 10N/kg x 20m
= 40 Joules.
So after the impact the ball loose 30J and the energy remaining is 40 J-10J
= 10 Joules
At the top of rebound the energy of the ball = potential energy (P.E)
The height reaches (h) is 5m.
Example 5
How much power is required to accelerate a 1000kg car from rest to 26.7m/s in 8sec?Solution:
The work done on the car increases its Kinetic energy.
Work done = AKE
½ MV2 – ½ MV2
The power required is given by:
Example 6
Car engine is rated in horsepower (hp) where 1hp = 746 watts. What is the required power measured in horsepower?Since work causes a change in energy. DE power can be considered as the rate of change of energy.
P = DE/t





0 Comments