Viruses were discovered by a Russian botanist D. I. Ivanovsky and a Dutchman Beijerink. In 1852 Ivanovsky prepared an infectious extract from tobacco plants that were suffering from mosaic disease.
When the extract was passed through a filter able to prevent the passage of bacteria, the filtered fluid was still infectious. 1898 Beijerink gave the name “virus” (in latin means, “poison”) to describe the infectious nature of certain filtered plant fluids.
1. They are the smallest living organisms ranging from 20-30 nm. On average, they are about 50 times smaller than bacteria.
2.Viruses do not have cellular structures, which mean that they lack certain important organelles like nucleus, cytoplasm, golgi bodies, etc.
3.They can only reproduce inside the living cells hence they are parasitic.
4.They have a simple structure consisting of either DNA or RNA but not both, surrounded by a protein or lipoprotein coat.
5.They can be described as living or non-living.
6.They are highly specific to their hosts i.e. each virus recognizes only certain types of cells.
7.Viruses are capable of replicating themselves only when they are inside the host cell.
Viruses as living things
1.They possess genetic material (RNA or DNA).2.They reproduce when they are in the host cell (replication).
3.They are capable of identifying their hosts and attack them.
4.They can undergo mutation (they mutate) i.e. they undergo different changes in shape.
5.Like other parasites, they are specific to host.
Viruses as non-living things
1.They can crystallize outside the host.2.They are metabolically inert in isolation.
3.They are non-cellular i.e. they lack cell organelles.
4.They do not perform necessary life processes such as respiration, excretion nutrition etc.
The Structure of Viruses
Generally viruses have a very simple structure consisting of the following:1.RNA or DNA which may be single stranded or double stranded. They form a structure called core.
2.A protective coat of protein surrounding the core called capsid.
3.A nucleocapsid which is a combined structure of core and capsid.
4.Envelope – an additional layer of lipoprotein layer around the capsid.
5.Capsids are made up of identical repeating units known as capsomeres.
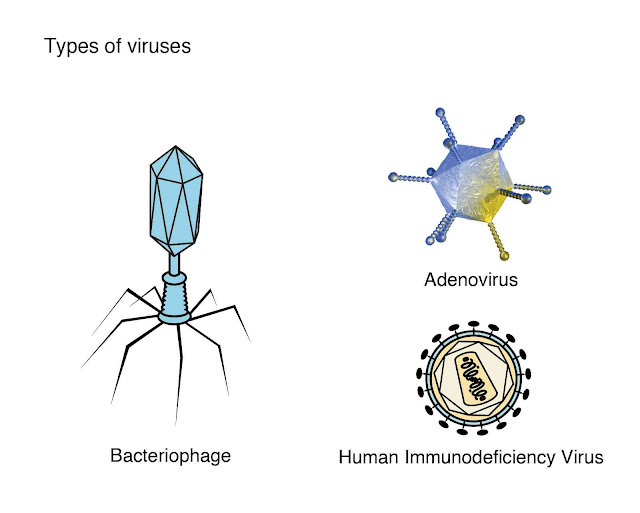
Bacteriophage
Bacteriophage is a virus that attacks and kills bacteria. Some of them have head with a tail sheath.Advantages and Disadvantages of Viruses
- Advantages of viruses
2.Viruses are used as biological weapons to kill organisms.
3.They are used as vectors in genetic engineering to transfer genes from one organism to another for improving or treating the defective genes.
4.Bacteriophages are viruses that attack bacteria and hence they help in controlling infections and diseases.
5.Viruses are used as biological weapons in wars and in biological pest control.
- Disadvantages of viruses
e.g. measles, small pox, poliomyelitis and yellow fever are caused by viruses.




0 Comments